Introduction: Vitamin D deficiency is a prevalent health concern that can have significant impacts on overall well-being. This blog post delves into the symptoms, causes, treatment, and benefits of Vitamin D deficiency, offering valuable insights for individuals looking to understand and address this essential health issue.
Table of Contents
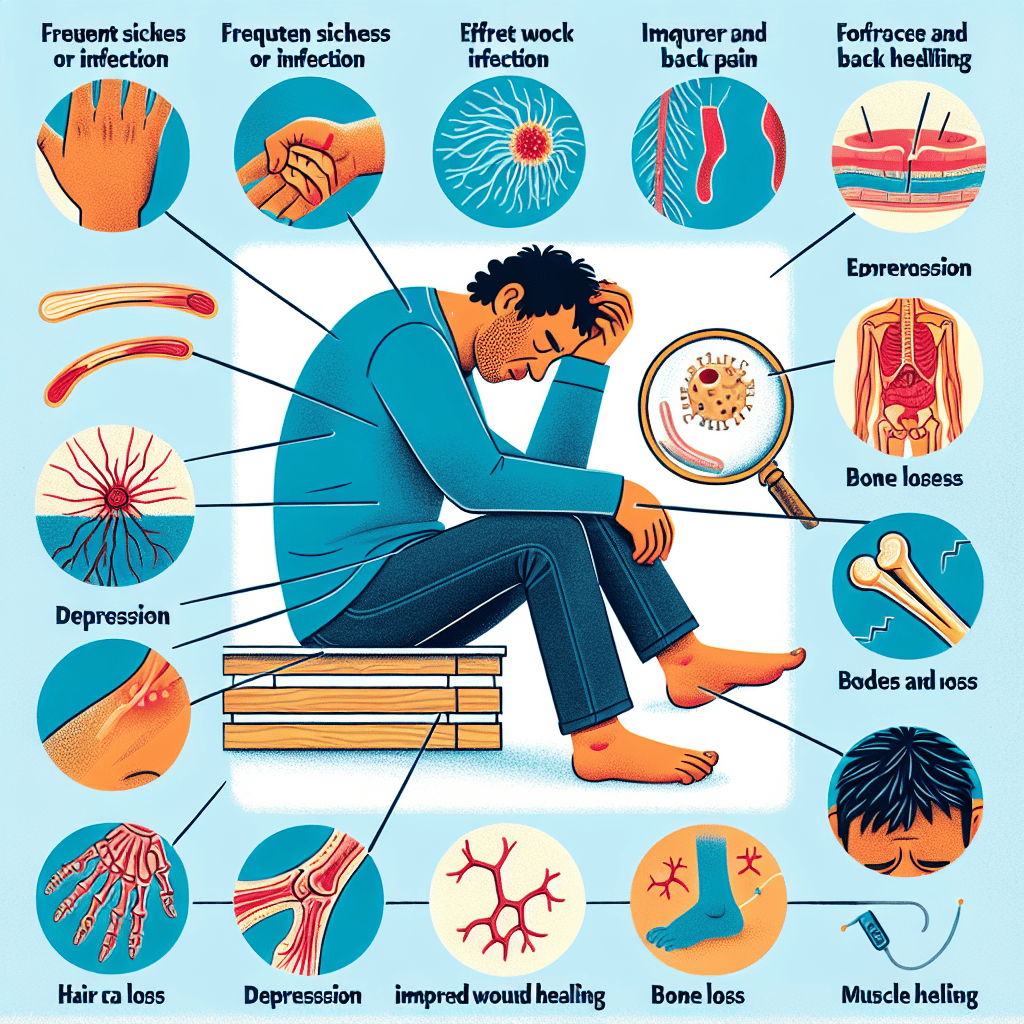
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Discover the various symptoms associated with Vitamin D deficiency in adults.
- Recurrent Disease and Infection:
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. One of the most well-known functions of vitamin D is its role in maintaining bone health. Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is important for maintaining strong and healthy bones. A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to bone problems such as osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones that are more prone to fractures. In addition to bone health, vitamin D also plays a role in immune function. Studies have shown that vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of colds, flu, and respiratory infections. This is because vitamin D helps regulate the immune response, making it an important factor in the body’s ability to fight off infections. By maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D, individuals can help reduce their risk of these common illnesses.
Apart from bone health and immunity, vitamin D also plays a role in wound healing and mood regulation. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to poor wound healing, as the nutrient is involved in the production of certain antimicrobial peptides that help the body fight off infections at the site of a wound. Additionally, vitamin D has been implicated in mental health, with low levels of the vitamin being associated with an increased risk of depression. This link is thought to be related to vitamin D’s role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating mood. Thus, ensuring adequate vitamin D levels through proper diet or supplementation may help support both physical and mental well-being.
Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency can also manifest in physical symptoms such as hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. While the exact relationship between vitamin D and hyperhidrosis is not fully understood, some studies have suggested that there may be a link between the two. It is believed that vitamin D may play a role in regulating sweat gland function, and a deficiency in the vitamin could potentially lead to overactive sweat glands and increased sweating. By maintaining optimal vitamin D levels, individuals may be able to help manage symptoms of hyperhidrosis and improve their overall quality of life.
- Bone Pain in Children:
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in ensuring the proper growth and development of children. When children suffer from a deficiency in Vitamin D, it can lead to various health issues. One common symptom of Vitamin D deficiency in children is bone pain. This can manifest as generalized aches or pains in the bones, particularly in the legs, joints, and back. The deficiency negatively impacts the body’s ability to maintain optimal bone health and can result in conditions like rickets, a disease that softens and weakens bones.
In addition to bone pain, inadequate levels of Vitamin D can also hinder a child’s growth and development. Children with Vitamin D deficiency may exhibit poor growth rates, both in terms of height and weight, compared to their peers. This deficiency can affect bone mineralization and lead to stunted growth. Delayed teething is another common indicator of Vitamin D insufficiency in children. Proper levels of Vitamin D are essential for dental health and the timely eruption of teeth. When children experience delays in teething, it can be a sign of underlying nutrient deficiencies, including Vitamin D.
Moreover, Vitamin D deficiency can weaken the immune system, making children more susceptible to infections. Insufficient levels of Vitamin D can impair the body’s ability to fight off pathogens, leading to increased infection risks. Behavioral disorders and mood changes are also linked to Vitamin D deficiency in children. Research suggests that low levels of Vitamin D may impact neurotransmitter function and contribute to conditions like depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children. Furthermore, Vitamin D plays a vital role in maintaining proper calcium levels in the body. Inadequate Vitamin D can disrupt calcium absorption, leading to potential issues like impaired bone health and calcium imbalances, which are crucial for various physiological processes in the body.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Understand the primary factors contributing to Vitamin D deficiency.
- Limited Sunlight Exposure:
Vitamin D deficiency is a common health concern that can result from various factors. Reduced exposure to sunlight is a primary cause because our skin produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Factors such as spending excessive time indoors, using sunscreen consistently, living in regions with limited sunlight, or covering the skin for cultural or religious reasons can all contribute to reduced sunlight exposure. Additionally, inadequate dietary intake of foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, can also lead to deficiency.
Digestive issues can impair the body’s ability to absorb vitamin D effectively, even if an individual is consuming sufficient amounts through their diet or sunlight exposure. Disorders like celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and cystic fibrosis can compromise the absorption of nutrients, including vitamin D, leading to deficiency over time. Furthermore, obesity is linked to vitamin D deficiency as the excess body fat can trap vitamin D, making it less available for the body to utilize. This means that individuals with obesity may require more vitamin D to maintain optimal levels compared to those with normal body weight.
Aging is another factor associated with vitamin D deficiency. As people age, their skin becomes less efficient at producing vitamin D from sunlight, making older adults more prone to deficiency. Moreover, dark skin pigmentation acts as a natural sunscreen, reducing the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight exposure. This means that individuals with darker skin tones may require more sunlight exposure to produce an adequate amount of vitamin D compared to those with lighter skin. Addressing these factors and ensuring sufficient intake of vitamin D through sunlight, diet, or supplements is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing deficiency-related complications.
Complications of Vitamin D Deficiency
Learn about the potential complications associated with prolonged Vitamin D deficiency.
- Cardiovascular and Autoimmune Diseases:
Vitamin D, commonly known as the sunshine vitamin, plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. One of its primary functions is to help the body maintain optimal levels of calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for bone health. However, research has also shown that Vitamin D deficiency can have far-reaching consequences beyond bone health. One significant risk associated with Vitamin D deficiency is an increased likelihood of developing heart disease. Studies have indicated that low levels of Vitamin D are linked to an elevated risk of hypertension, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular issues.
In addition to heart disease, Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of stroke. Research suggests that individuals with insufficient Vitamin D levels may be more prone to blood vessel damage and clot formation, which are common underlying causes of stroke. Furthermore, autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes, have also been linked to inadequate Vitamin D levels. The vitamin is believed to play a role in modulating immune system function, and its deficiency may contribute to the development or worsening of autoimmune conditions.
Moreover, neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s have also been connected to Vitamin D deficiency. The vitamin is thought to have neuroprotective properties and may help in reducing inflammation in the brain, which are believed to be factors in the development of these neurodegenerative disorders. Pregnant women with low levels of Vitamin D are at a higher risk of experiencing complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and premature birth. Additionally, certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer, have shown associations with Vitamin D deficiency. While more research is needed to fully understand the link between Vitamin D and cancer, maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin D through sunlight exposure, diet, and supplements is considered important for overall health and disease prevention.
Treatment for Vitamin D Deficiency
Explore the treatment options available to address Vitamin D deficiency.
- Dietary Supplements and Injections:
Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in maintaining overall health. It helps in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for maintaining strong bones and teeth. Vitamin D also supports the immune system, helps in cell growth, and reduces inflammation. However, many people may struggle to maintain adequate levels of Vitamin D through diet and sun exposure alone.
Supplements in the form of Vitamin D2 and D3 are commonly used to address deficiencies and maintain optimal Vitamin D levels. Vitamin D2, also known as ergocalciferol, is derived from plant sources, while Vitamin D3, also called cholecalciferol, is synthesized in the skin upon exposure to sunlight or obtained from animal sources. Both forms are effective in increasing Vitamin D levels in the body, with Vitamin D3 generally being more potent and longer-lasting. In cases of severe Vitamin D deficiency, healthcare providers may recommend high-dose injections to quickly raise Vitamin D levels in the bloodstream.
Regular monitoring of Vitamin D levels through blood tests is essential to determine the effectiveness of supplementation and ensure that levels stay within the optimal range. It’s important to follow healthcare provider recommendations regarding dosage and duration of supplementation, as excessive Vitamin D intake can lead to toxicity. While supplements and injections can be instrumental in restoring Vitamin D levels, it’s also advisable to incorporate Vitamin D-rich foods such as fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks into the diet. Additionally, spending time outdoors in sunlight and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels naturally.